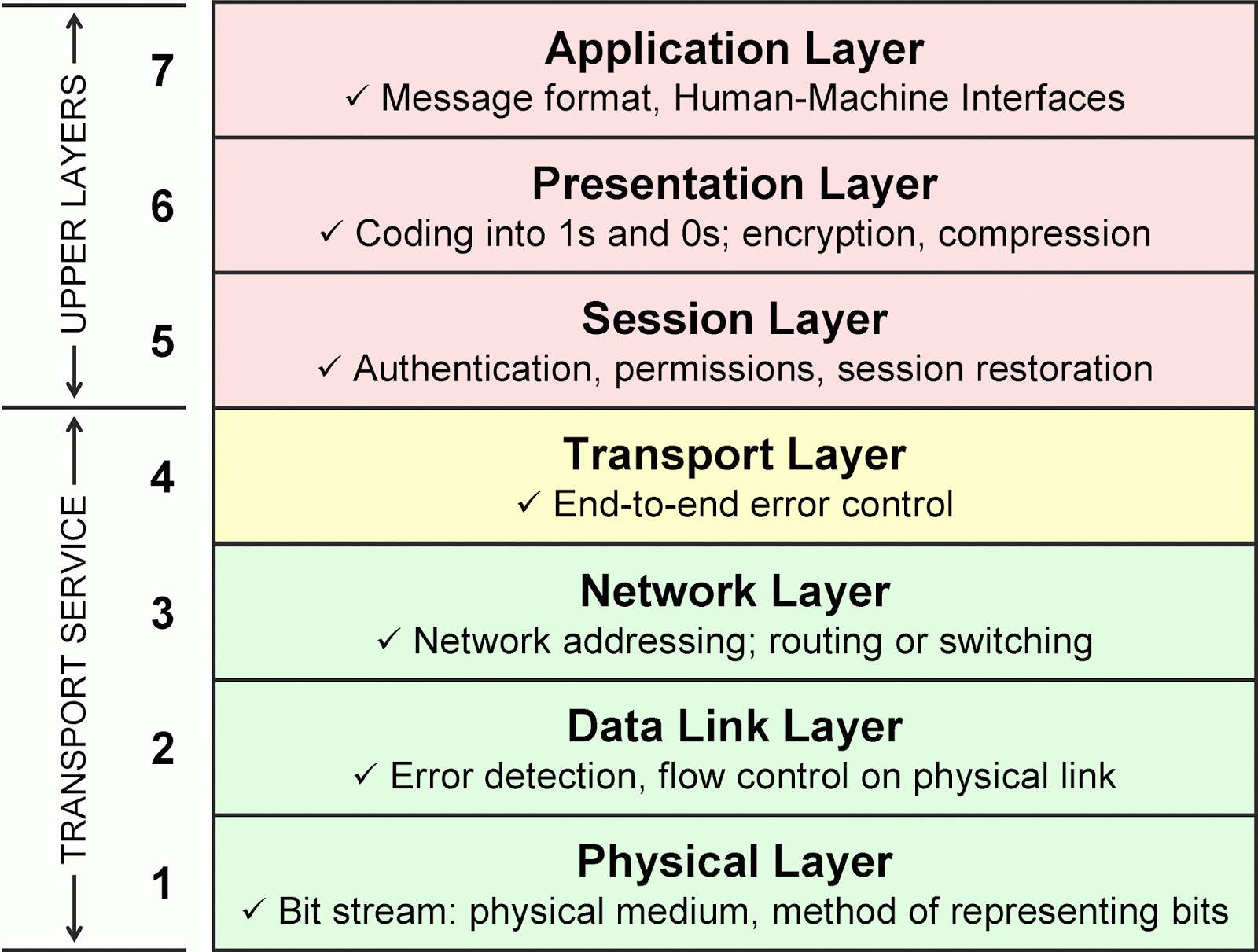
Open System Interconnect (OSI) Reference Model
Why Layer Model
- Reduces complexity
- Standardizes interfaces
- Facilitates modular engineering
- Ensures interoperate technology Ensures interoperate technology
- Accelerates the evolution of network technology.
- Simplifies teaching and learning
OSI Model – Physical Layer
- deals with mechanical, electrical and procedural interfacing.
- specifies cables, connectors, and other components.
- transmits raw information over communication channel communication channel.
- establishes, maintains, and disconnects physical links physical links.
OSI Model – Data Link Layer
- provides reliable transfer of data
- breaks data (packets) into frames
- adds bits for error detection/correction
- manages access to and use of the manages access to and use of the channel
- solve problems caused by lost, damaged, and duplicate frames
- sends acknowledgments
- adds flags to indicate beginning and end of message
- connectionless or connection oriented connectionless or connection oriented services
- IEEE MAC and LLC support
OSI Model – Network Layer
- establishes, maintains and terminates connections
- determines how packets are routed
- divides transport messages into packets divides transport messages into packets and reassembles them
- performs congestion control flow control performs congestion control, flow control.
- provides virtual circuit or datagram services
- recognizes message priorities
- sends messages in proper order
- handles internetworking
OSI Model – Transport layer
- establishes reliable end-to-end transport session (error detection and recovery), once path has been established
- fragmentation of message into packets (if not handled by layer 3)
- multiplexing of several sessions from multiplexing of several sessions from same source and all going to same destination
OSI Model – Session layer
- establishes and terminates connections
- accounting service
- authentication of users
- controls dialogue, organizes and synchronizes
OSI Model – Presentation layer
- data encryption, security, compression and code conversion
- make sure data is encoded in standard form ( ASCII)
- handles pass-through of services from session to application layer session to application layer
OSI Model – Application layer
- login, password check
- agreement on semantics for information exchange
- file transfer access and management file transfer, access and management
- message handling, email
- job transfer and manipulation
- directory service
No comments:
Post a Comment